The thermal expansion valve controls the opening of the expansion valve through the superheat of the gaseous refrigerant at the evaporator outlet, so it is widely used in the non-full liquid evaporator. According to the different balance methods, the thermal expansion valve can be divided into internal balance type and external balance type. The temperature sensing system of the thermal expansion valve can be filled with different substances and methods, including liquid filling, gas filling, cross filling, mixed filling, and adsorption filling.
1. Adjustment skills and taboos of the thermal expansion valve
In order for the thermal expansion valve to perform the automatic regulation function under one working condition, it must be adjusted during the commissioning of the refrigeration system, to ensure that the thermal expansion valve can correctly perform the automatic regulation during the system operation. The expansion valve adjustment is realized through the adjusting rod. The screwing or screwing out of the adjusting rod is essentially the pressing or loosening of the spring, that is, the adjustment of the static assembly superheats of the thermal expansion valve to meet the needs of the refrigeration conditions. Generally, clockwise rotation means to advance and reverse rotation means to retreat. When the evaporation pressure is to be adjusted, the cap can be removed, and the adjusting rod can be turned clockwise with a wrench to increase the compression of the spring, force the diaphragm to move up and close the valve, and the evaporation pressure will gradually drop. In the same way, reverse rotation of the regulating rod will open the valve and increase the evaporation pressure.
When adjusting the thermal expansion valve, a low-pressure gauge should be installed on the suction stop valve of the compressor to observe the change in evaporation pressure. The normal evaporation pressure is frosting or condensation to the suction pipe (frosting of medium and low-temperature equipment; condensation of air conditioning equipment). If frost or condensation forms on the suction stop valve or even half of the compressor, it means that the valve is too large and should be turned down. If the frost or condensation only forms on the evaporator outlet or does not form on the outlet, it means that the valve is too small and should be turned up.
The commissioning of the thermal expansion valve can generally be carried out in two steps. In the beginning, it is a coarse adjustment, that is, it can rotate about one circle each time. When the equipment is close to its operating condition, fine adjustment shall be carried out, with each rotation of 1/4~1/2 turns. After each adjustment, the system should be operated for several minutes or more, and the change of the low-pressure gauge should be observed before deciding on the next adjustment. At the end of the expansion valve commissioning, the cap should be screwed on and tightened with a wrench to prevent refrigerant leakage. Adjusting the thermal expansion valve is meticulous work. Do not be impatient during the adjustment process. The adjusted thermal expansion valve shall not be adjusted for other reasons unless the operating condition of the refrigerator is changed. Generally, the thermal expansion valve of the unit delivered from the factory has been adjusted before delivery, and the unit shall not be adjusted during on-site commissioning.
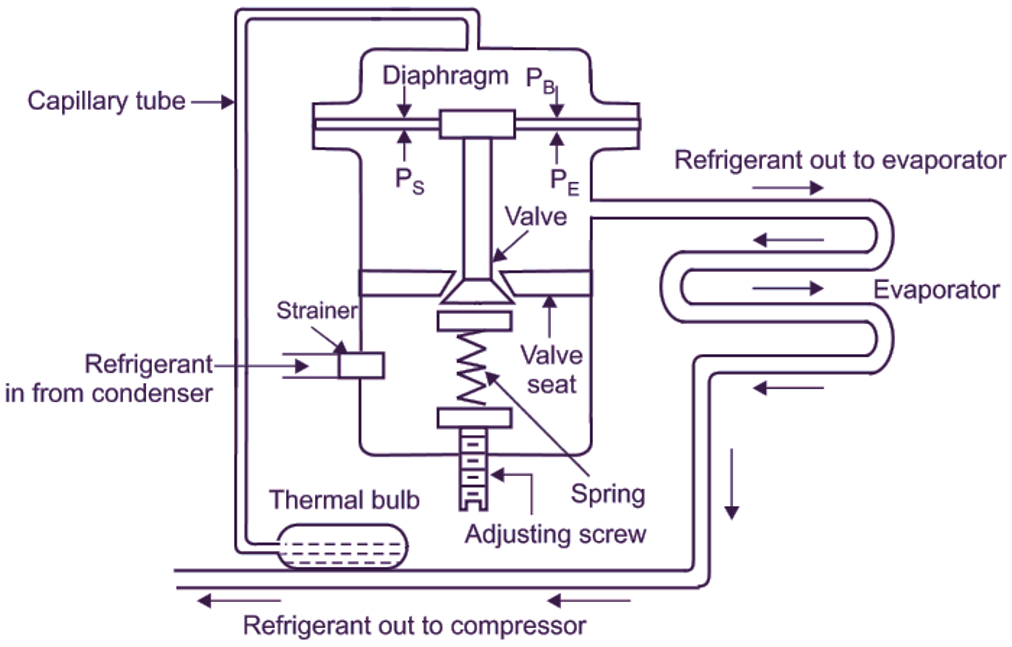
2. Maintenance operation of the thermal expansion valve
The common faults of the thermal expansion valve include blockage, leakage of the working medium of the temperature sensing bag, etc. The blockage of the valve hole includes ice blockage and oil blockage.
If there is water in the refrigeration system, it will be dissolved in the refrigerant. Its dissolution is related to the temperature of the refrigerant. If the temperature is high, its dissolution is large, and if the temperature is low, its dissolution is small. When the refrigerant liquid with a condensation temperature of about 30t flows into the expansion valve orifice for throttling, it immediately cools to the saturation temperature (evaporation temperature) under the evaporation pressure, and some water is separated. If the evaporation temperature is below 0 ℃, the part attached to the valve orifice will form an ice layer. When the ice layer increases, the valve orifice will be blocked.
The refrigerant oil and refrigerant will also dissolve each other, and the amount of dissolution is also related to temperature. The amount of dissolution is large at high temperatures but small at low temperatures. When the liquid enters the expansion valve hole and its temperature drops rapidly after throttling, part of the refrigerant oil is separated and stuck around the valve hole. When the evaporation temperature is lower than the freezing point of the refrigerant oil, the refrigerant oil will condense into a paste. When the oil gradually increases, the valve hole will be blocked because the lower the evaporation temperature is, the easier the water and oil will be separated, so ice blockage and oil blockage can easily occur in low-temperature refrigeration equipment with lower evaporation temperatures.
Judgment of valve hole ice blockage or oil blockage: when the refrigeration unit starts to operate normally for some time, the suction pressure drops rapidly to negative pressure (vacuum), the temperature of the warehouse (chamber) rises, the frost layer melts (first, the frost layer of the suction pipe melts), and the flow sound of the expansion valve can not be heard in the ear. At this time, it can be determined that the valve hole is blocked by ice or oil. In order to further confirm that the valve hole is blocked, the expansion valve body can be heated with an alcohol lamp (without shutdown). After heating for one or two minutes, if the sound of airflow is heard, then the sound of creaking can be heard, the suction pressure also rises, and the outlet of the expansion valve starts to white again, indicating that the valve hole is indeed blocked by ice or oil.
Post time: Feb-14-2023

