+86-13376814803
+86-13376814803  robert@hzhongtai.com
robert@hzhongtai.com
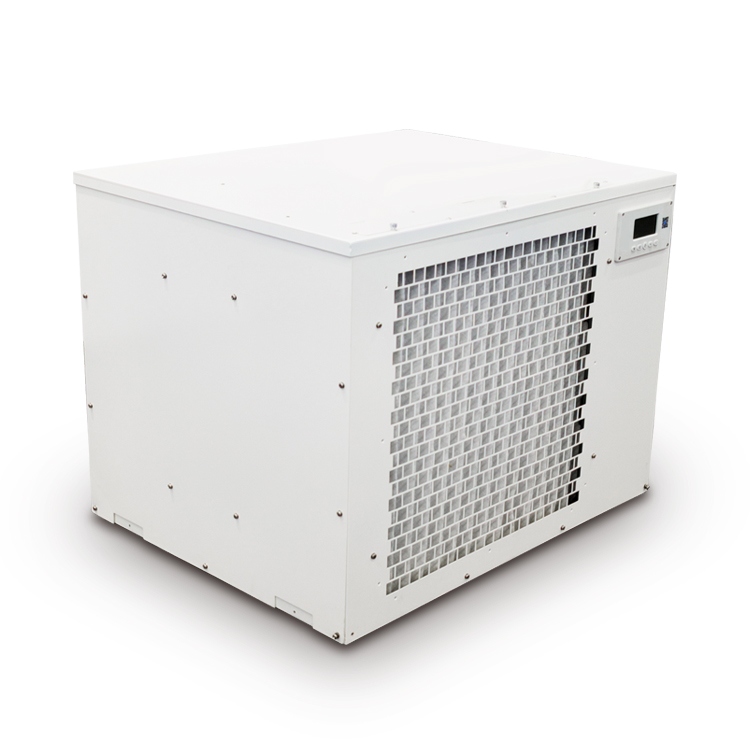
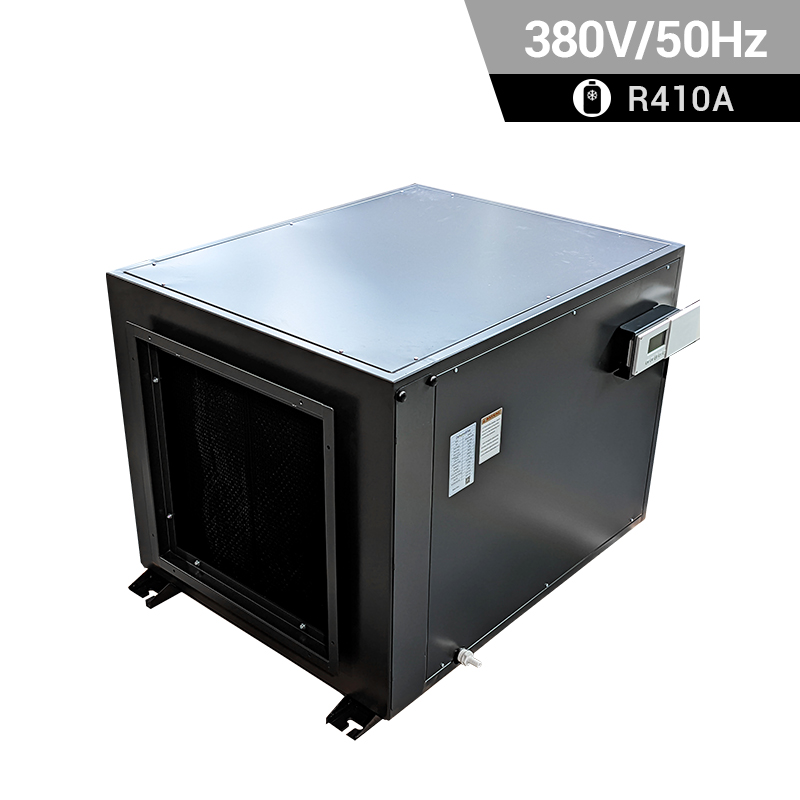
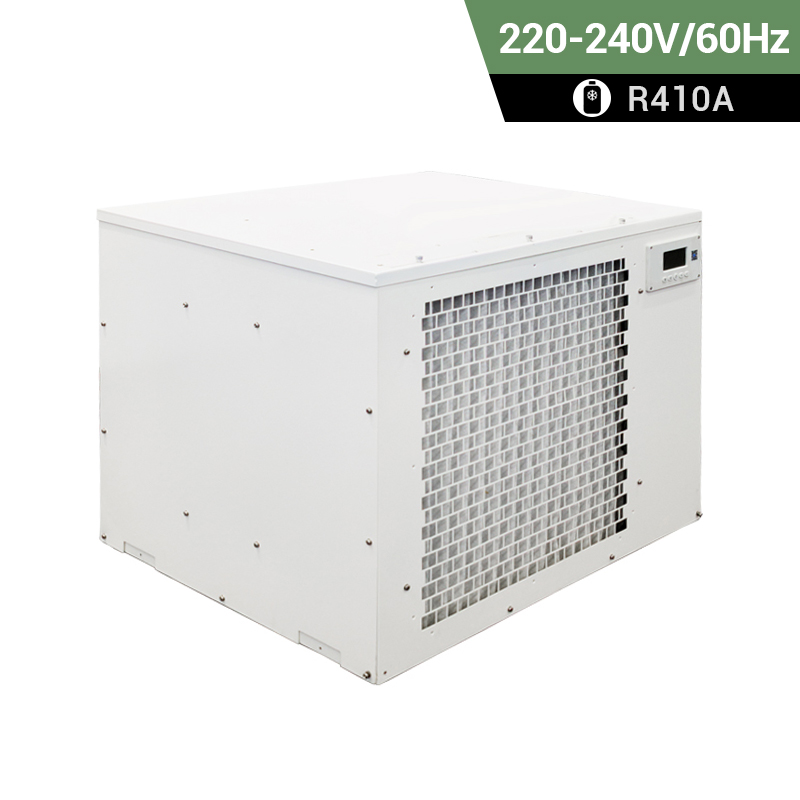
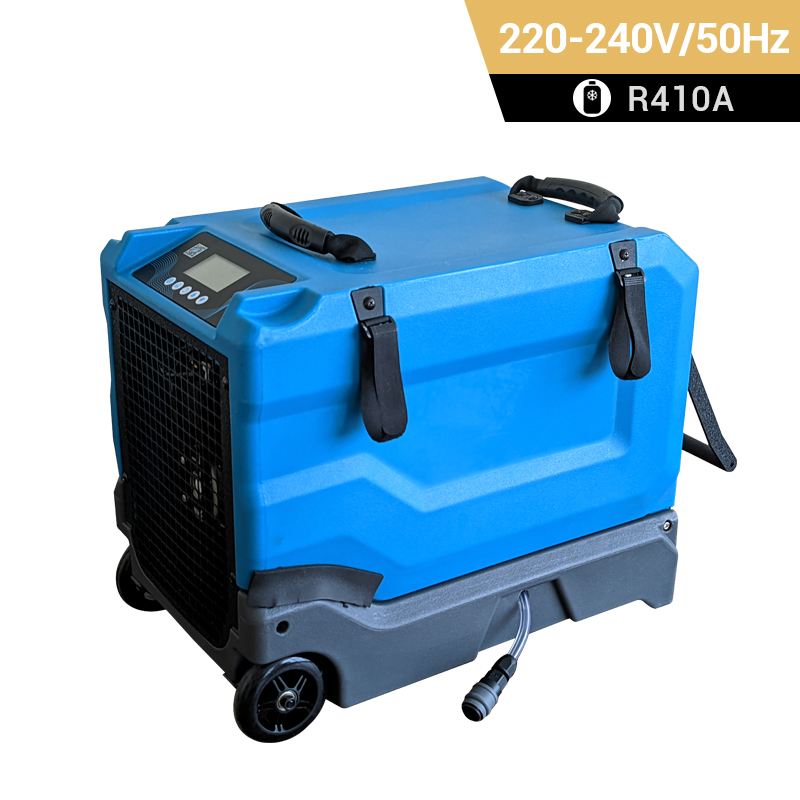
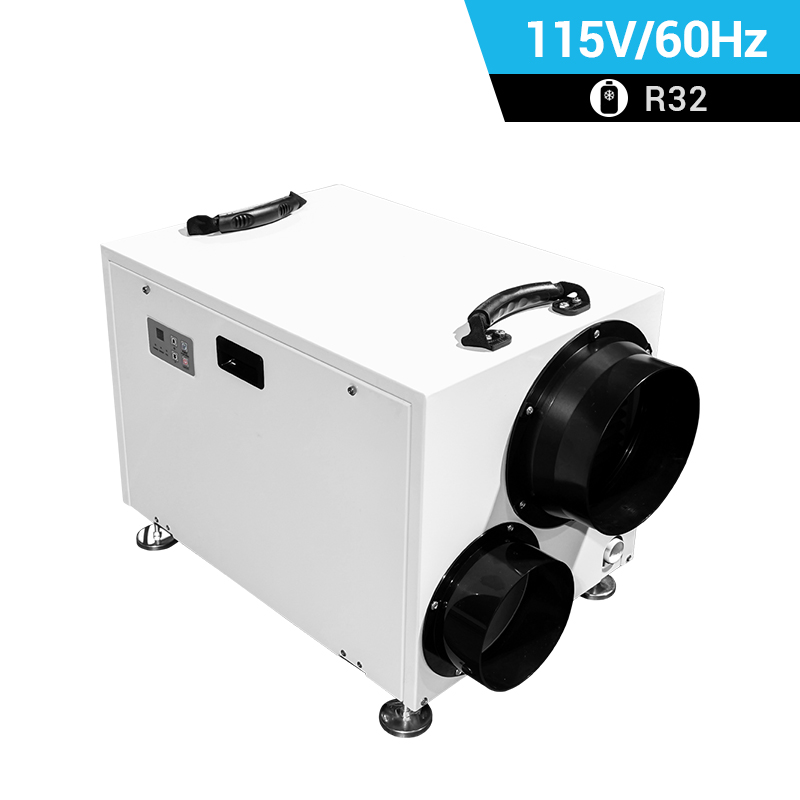
Heat Pump
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one place to another, typically from a lower-temperature space to a higher-temperature space. It can be used for both heating and cooling purposes, making it a versatile technology for maintaining comfortable temperatures in buildings.
There are two main types of heat pumps:
-
Air Source Heat Pump (ASHP): This type of heat pump transfers heat between the inside of a building and the outside air. It extracts heat from the outdoor air during the heating season to warm the interior of a building and reverses the process during the cooling season to remove heat from the indoor air and release it outside.
-
Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) or Geothermal Heat Pump: This type of heat pump transfers heat between the building and the ground. It utilizes the relatively stable temperature of the ground or groundwater to efficiently heat or cool a space. The ground source heat pump is generally more energy-efficient than an air source heat pump, but it often involves more complex installation and is associated with higher upfront costs.
Here's how a typical heat pump works:
-
Heating Mode: In heating mode, the heat pump extracts heat from the outside air (or ground) and transfers it indoors. The refrigerant in the heat pump's coils absorbs heat from the outdoor air, and then, through a compressor, the temperature of the refrigerant increases. The heated refrigerant is then circulated indoors, and a fan or blower distributes the heat throughout the building.
-
Cooling Mode: In cooling mode, the process is reversed. The heat pump extracts heat from the indoor air and releases it outside. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air, and the compressor raises the temperature of the refrigerant. The heat is then expelled outside, and the cooled refrigerant is circulated back indoors to absorb more heat.
Benefits of heat pumps include:
-
Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps can be more energy-efficient than traditional heating and cooling systems, especially in moderate climates.
-
Versatility: Heat pumps provide both heating and cooling functions, eliminating the need for separate systems.
-
Reduced Environmental Impact: Heat pumps can be environmentally friendly, especially if they use renewable electricity sources.
-
Consistent Temperature Control: Heat pumps are designed to provide consistent and comfortable indoor temperatures.
It's important to note that the efficiency of a heat pump can be influenced by factors such as the climate, the specific type of heat pump, and the quality of installation. Consulting with a professional HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) technician can help determine the best heat pump solution for a particular environment.
Related Products