+86-13376814803
+86-13376814803  robert@hzhongtai.com
robert@hzhongtai.com
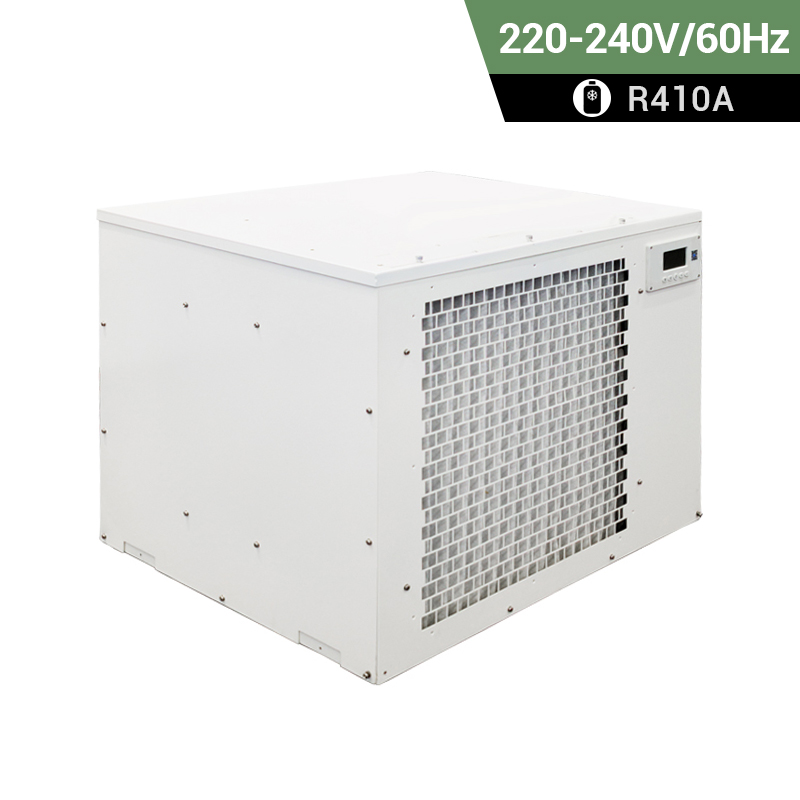
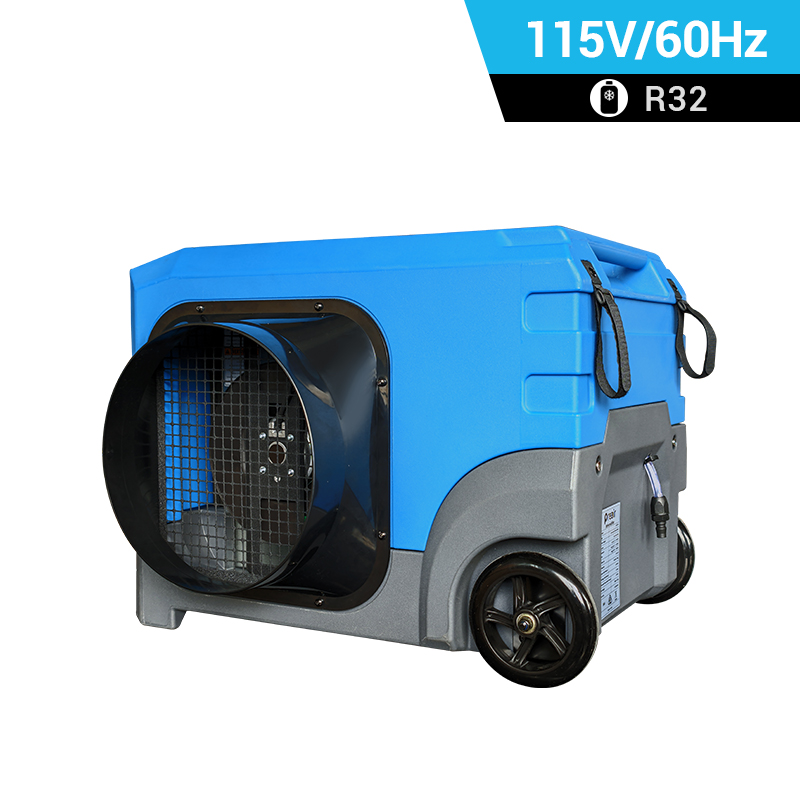
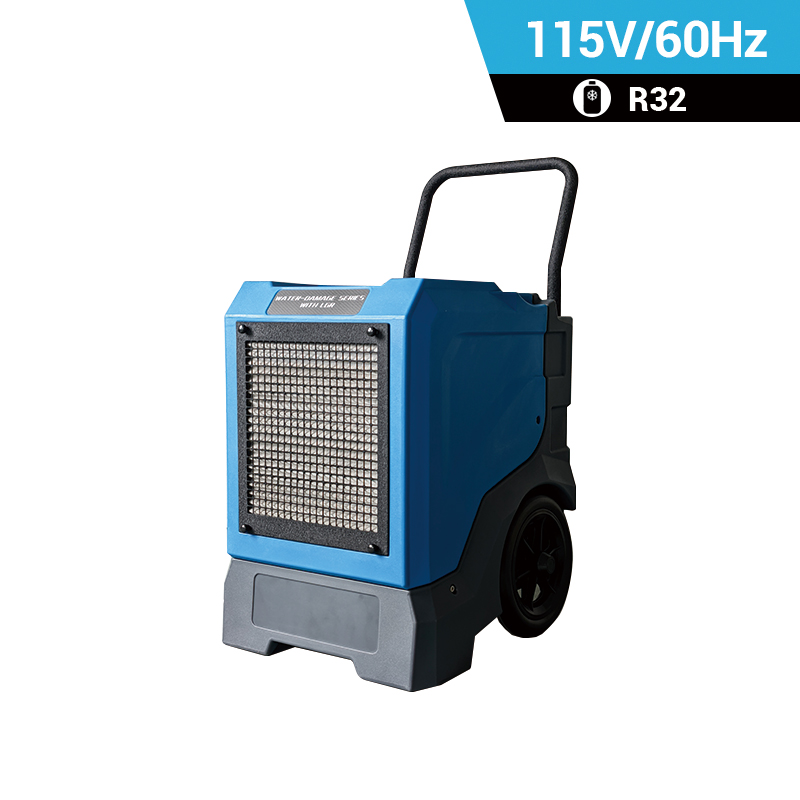
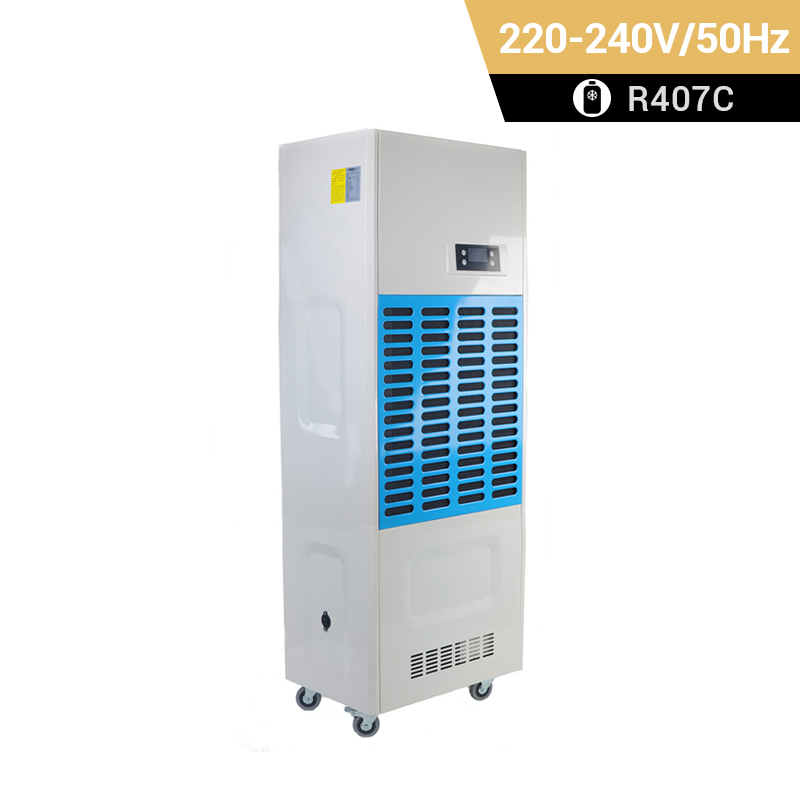
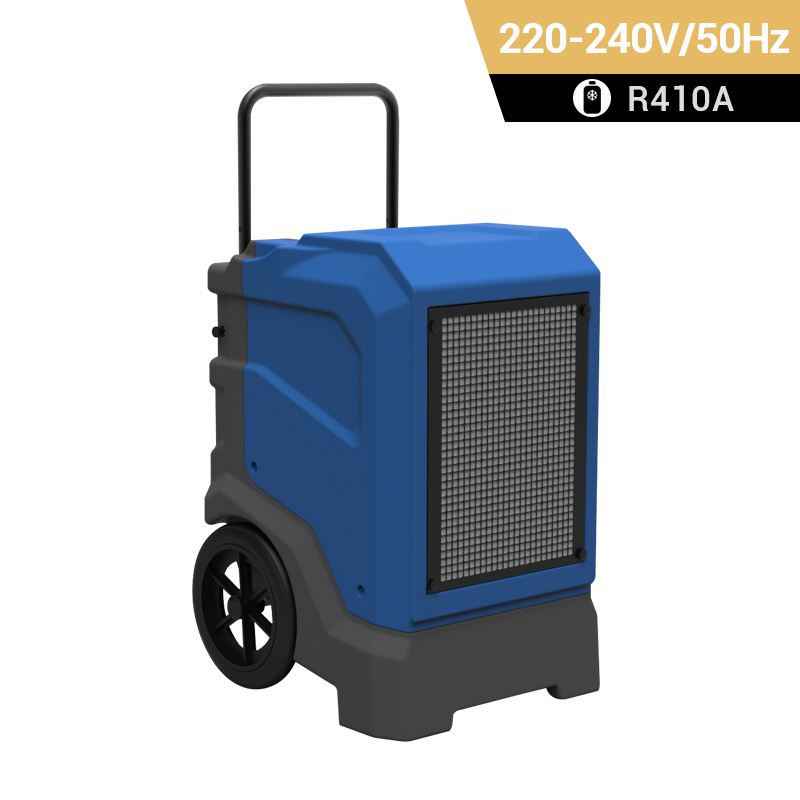
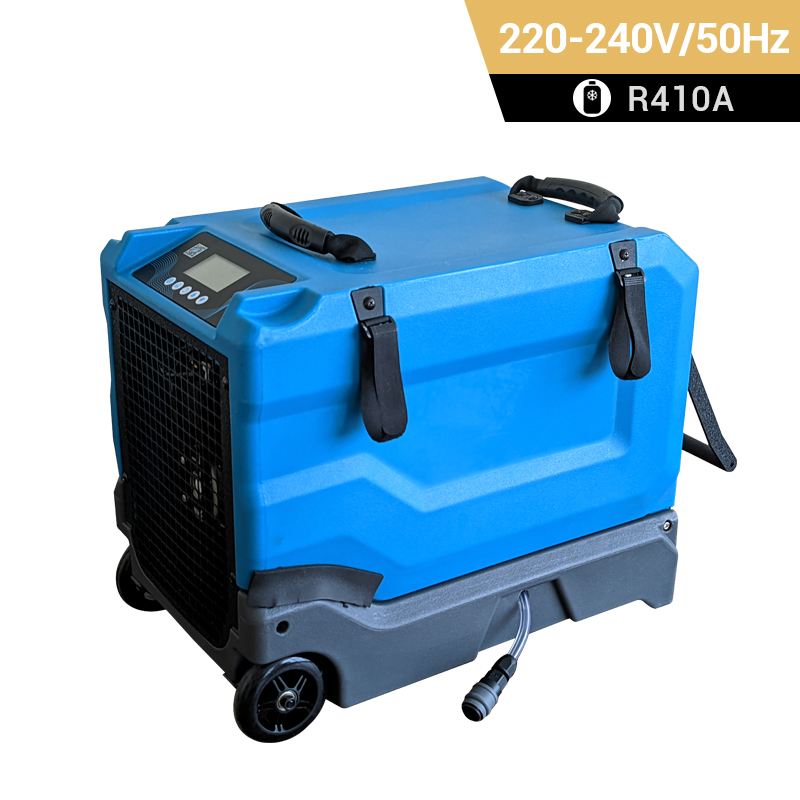
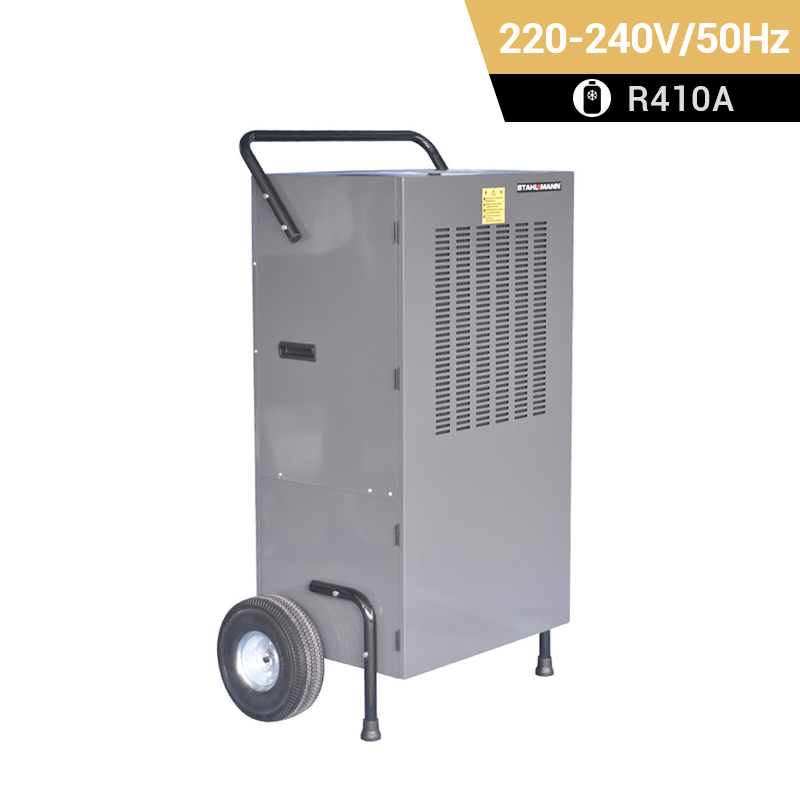
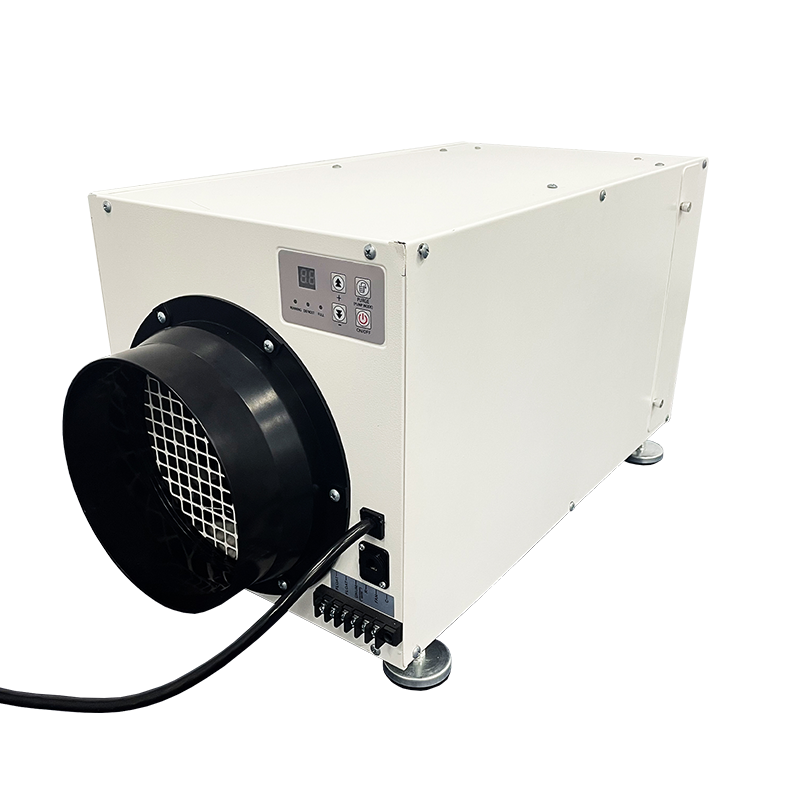
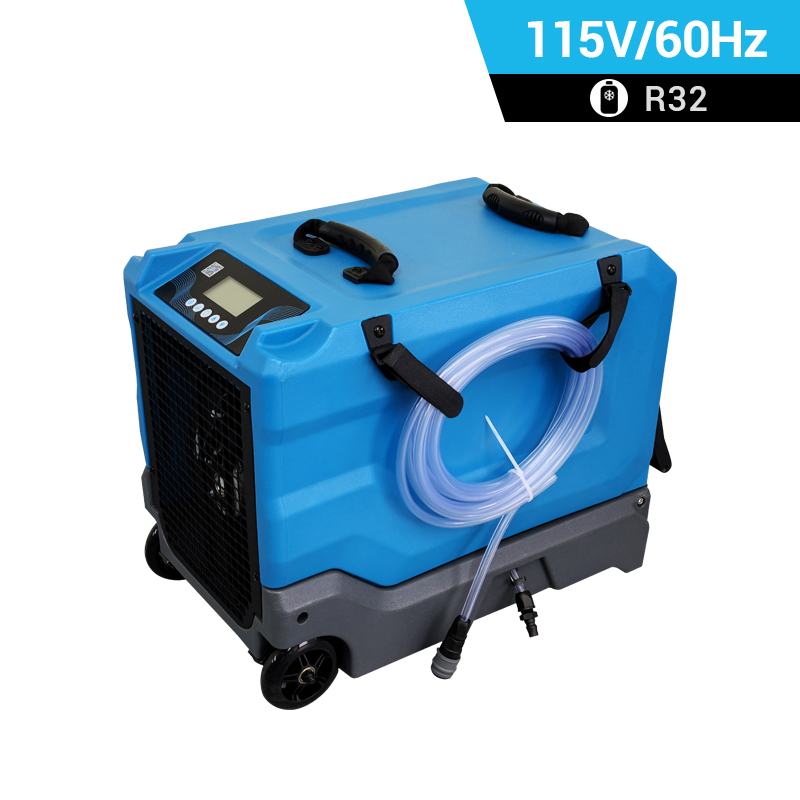
dehumidifier for plant room
Should I use a humidifier or dehumidifier for grow tent?
Humidity has a significant impact on the transpiration, photosynthesis, disease occurrence, and physiological imbalance of greenhouse crops, specifically manifested in:
1. Air humidity affects transpiration. Transpiration is not only the power of plant water absorption, but also the power of mineral nutrition transportation. With high air humidity and weak transpiration, the ability of plants to transport mineral nutrients will decline. Transpiration can also adjust the temperature of leaves. If the temperature is high, the air humidity is high, and transpiration is weak, the leaves may be burned.
2. The size of air humidity can affect the opening and closing of plant stomata. Excessive or insufficient air humidity can lead to stomatal closure, preventing carbon dioxide from entering mesophyll cells, and slowing or even stopping photosynthesis.
3. Excessive air humidity is beneficial for the reproduction of bacteria, and most fungal spores require high humidity for germination and hyphal development; Low temperature is conducive to the occurrence of pests, such as mites such as red spiders, which generally occur in high temperature and low humidity environments.
4. High humidity can cause water condensation on the leaf surface, causing cell rupture and weakening of the plant.
Relative humidity has a significant impact on plant growth. It is best to equip dehumidifiers for grow tents to accurately control humidity. Preair is a reliable industrial dehumidifier manufacturer that produces the ZETA series and PRO series dehumidifiers fot greenhosue.
Related Products